Oral cancer screenings are an essential component of preventive healthcare, offering a critical opportunity for early identification of malignancies. This early detection is pivotal, as it substantially enhances treatment success and survival rates. Dental professionals are uniquely positioned to perform these screenings during routine check-ups, identifying risk factors and symptoms often overlooked by patients. With advances in technology improving detection methods, the question remains: how can we optimize these screenings to further reduce oral cancer morbidity and mortality?
Understanding Oral Cancer: Key Facts and Statistics
Oral cancer, a significant health concern, encompasses malignancies that occur in the mouth and pharynx, accounting for approximately 3% of all cancers diagnosed annually in the United States. The oral cancer prevalence has remained stable, yet it continues to pose challenges due to its late-stage diagnosis. Epidemiological data reveal that males are disproportionately affected, with higher incidence rates compared to females, and tobacco use remains a notable risk factor. Survival rates are contingent upon the stage at diagnosis; early detection correlates with a five-year survival rate of approximately 84%, whereas advanced stages result in a marked decrease to around 39%. These statistics underscore the importance of understanding the demographics and prognosis associated with oral cancer to inform clinical strategies effectively.
The Importance of Early Detection in Oral Cancer
Early detection of oral cancer markedly enhances patient prognosis by identifying malignancies at a more treatable stage. Screening methods, including visual examinations and adjunctive diagnostic tools, are vital for identifying early signs such as persistent sores, lumps, or red and white patches. The benefits of early detection are underscored by increased survival rates and reduced morbidity, emphasizing the need for routine screenings in at-risk populations.
Signs of Oral Cancer
Despite being highly treatable when detected early, oral cancer often progresses unnoticed due to subtle initial symptoms. Early warning signs include persistent oral sores, unexplained bleeding, or white/red patches on oral mucosa. Symptom recognition is vital; difficulty in swallowing, persistent sore throat, and changes in voice may indicate pathology. Clinically, non-healing ulcers or lesions persisting beyond two weeks warrant immediate evaluation. Evidence suggests these manifestations may precede more conspicuous symptoms, such as noticeable lumps or significant weight loss. In addition, risk factors like tobacco use, alcohol consumption, and human papillomavirus (HPV) infection correlate with increased symptom prevalence. Identifying these early warning signs through vigilant clinical assessment is essential for prompt intervention, potentially improving patient prognosis and reducing morbidity associated with advanced-stage oral malignancies.
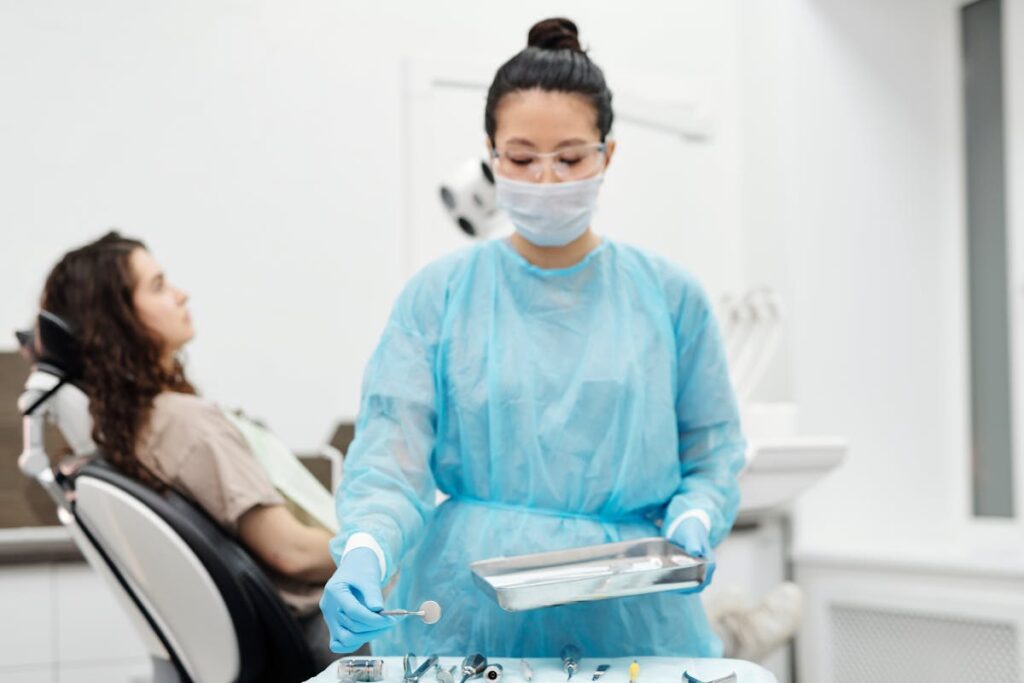
Screening Methods Explained
When detected early, oral cancer has a substantially higher treatment success rate, emphasizing the critical role of effective screening methods. Clinicians employ various screening techniques to identify potential malignancies at an initial stage, enhancing diagnostic accuracy. Visual examination remains fundamental, where practitioners assess the oral cavity for lesions or abnormalities. Adjunctive diagnostic tools, such as toluidine blue staining and brush biopsies, augment the visual inspection by highlighting atypical cells. Advanced imaging techniques like fluorescence visualization and narrow band imaging offer enhanced detection capabilities by illuminating suspect tissue areas. Additionally, emerging technologies, such as salivary biomarkers, present promising non-invasive methods for early-stage detection. These collective approaches underscore a multi-faceted strategy, integrating traditional and innovative methods to improve diagnostic precision in oral cancer screenings.
Benefits of Early Detection
Recognizing the critical impact of early detection, oral cancer screenings play an essential role in reducing morbidity and mortality rates associated with the disease. Scientific evidence underscores that early intervention greatly enhances treatment outcomes, as lesions identified at initial stages are often less invasive and more responsive to therapeutic strategies. Early detection facilitates the implementation of preventive measures, potentially halting the progression to advanced malignancy. Clinical studies reveal that timely screenings can result in a higher five-year survival rate, compared to diagnoses made at later stages. Furthermore, early identification minimizes extensive surgical procedures and the need for aggressive treatments, thereby improving patients’ quality of life. Consequently, integrating routine oral cancer screenings into standard dental practice is paramount in preventive healthcare.
How Oral Cancer Screenings Are Performed
Oral cancer screenings are systematically conducted procedures designed to detect early signs of cancerous or precancerous conditions in the oral cavity. Screening techniques typically involve visual examination and palpation of the oral tissues, including the lips, gums, tongue, and throat. Advanced methods, such as fluorescence visualization and toluidine blue staining, may be employed to enhance detection sensitivity. Prior to the examination, patient preparation is vital; it involves obtaining a thorough medical history and removing dental appliances to allow unobstructed access to oral tissues. Clinicians may also advise patients to abstain from consuming food or beverages that could obscure mucosal surfaces. These procedures are essential in identifying lesions that may warrant further diagnostic evaluation, ensuring prompt intervention and management.
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
Early detection of oral cancer greatly enhances treatment outcomes, making it critical to recognize the signs and symptoms indicative of the disease. Clinicians should be vigilant for persistent ulcers, leukoplakia, erythroplakia, and unexplained bleeding within the oral cavity. Such manifestations may suggest underlying malignancies affecting oral health. Additionally, patients may report dysphagia, odynophagia, or persistent hoarseness. These symptoms warrant thorough examination and possibly biopsy for definitive diagnosis. Clinical evidence suggests that early identification correlates with improved prognosis. Lifestyle changes, such as cessation of tobacco and alcohol use, have been shown to reduce symptom severity and recurrence risk. Consequently, healthcare providers should advocate for regular screenings and educate patients on recognizing early signs to enhance preventive care efforts.
Risk Factors Associated With Oral Cancer
Oral cancer risk is greatly influenced by behavioral and viral factors, prominently including tobacco and alcohol consumption and human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. Epidemiological studies consistently demonstrate that individuals who engage in tobacco use, whether smoking or smokeless, and excessive alcohol intake face a markedly increased risk for developing oral malignancies. Additionally, the oncogenic strains of HPV, particularly HPV-16, have emerged as a critical etiological factor, underscoring the importance of vaccination and early detection strategies in mitigating HPV-associated oral cancer incidence.
Tobacco and Alcohol Usage
How greatly do lifestyle choices impact the risk of developing oral cancer? Evidence indicates a significant correlation between the consumption of tobacco and alcohol and the incidence of oral cancer. Tobacco usage, in various forms, exposes the oral cavity to carcinogenic substances, elevating cancer risk. Concurrently, alcohol acts as a solvent, enhancing the oral mucosal absorption of these carcinogens. Studies have demonstrated that individuals who smoke and consume alcohol have a multiplied risk factor compared to non-users. Clinically, tobacco cessation and alcohol moderation are imperative strategies for reducing this risk. Encouraging patients to adopt these measures can substantially decrease oral cancer incidence. Healthcare providers should prioritize these interventions within preventive care protocols to mitigate associated oral cancer risks effectively.
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Influence
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) represents a considerable etiological factor in the development of oral cancer, particularly oropharyngeal cancers. Epidemiological studies have demonstrated a rising incidence of HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancers, attributed primarily to HPV transmission through orogenital contact. The presence of high-risk HPV strains, particularly HPV-16, is associated with malignant transformation of epithelial cells in the oropharyngeal region. Clinicians emphasize the importance of HPV vaccination as a preventive measure, which has shown efficacy in reducing the incidence of HPV-related cancers. The prophylactic administration of the HPV vaccine before the onset of sexual activity can considerably decrease HPV transmission rates. Consequently, integrating HPV vaccination into public health strategies is pivotal in mitigating the burden of HPV-associated oral malignancies.
The Role of Dental Professionals in Oral Cancer Prevention
Dental professionals play a pivotal role in the early detection and prevention of oral cancer, a critical aspect of patient care that can greatly influence outcomes. Through extensive dental education, practitioners are equipped to identify potential malignancies during routine examinations, considerably enhancing patient awareness. Evidence indicates that increased patient awareness leads to earlier diagnosis, thereby improving prognosis and survival rates. Dental professionals must continually update their knowledge and skills regarding oral cancer pathophysiology and risk factors. Regular participation in continuing education programs is essential to maintain diagnostic acumen. Additionally, by educating patients about risk factors such as tobacco use and human papillomavirus (HPV), dental practitioners can foster informed decision-making, ultimately reducing incidence rates. This proactive approach underscores the importance of the dental profession in cancer prevention strategies.
Integrating Oral Cancer Screenings Into Routine Dental Care
Oral cancer screenings, an essential component of routine dental care, enhance early detection and improve patient outcomes. The incorporation of systematic screenings into dental check-ups represents a proactive approach in preventive care. Evidence suggests that integrating these assessments within routine visits facilitates collaborative care, enabling dental professionals to work alongside oncologists and primary care providers. This multidisciplinary approach guarantees thorough management of oral health. Patient education plays a significant role; educating individuals about risk factors and symptoms empowers them to participate actively in their oral health maintenance. Studies indicate that informed patients are more likely to adhere to recommended follow-ups and screenings. Consequently, routine screenings, coupled with robust patient education, are pivotal in reducing the morbidity and mortality associated with oral cancer.
Advances in Technology for Oral Cancer Detection
As technological innovations continue to evolve, they greatly enhance the effectiveness and accuracy of oral cancer detection methods. Salivary biomarkers have emerged as a non-invasive diagnostic tool, offering promising results for early identification of malignant changes. These biomarkers can detect specific proteins and genetic alterations associated with oral carcinogenesis, providing clinicians with a molecular-level insight that aids in timely intervention. Concurrently, advanced imaging technologies, including optical coherence tomography and fluorescence imaging, enable detailed visualization of oral tissues. These imaging modalities facilitate the identification of abnormal lesions with high specificity and sensitivity, surpassing traditional examination techniques. By integrating salivary biomarker analysis and state-of-the-art imaging technologies, healthcare professionals can greatly improve diagnostic precision and potentially reduce oral cancer morbidity and mortality.
Encouraging Regular Screenings for Better Health Outcomes
While technological advancements greatly enhance diagnostic capabilities for oral cancer, the importance of regular screenings remains vital in achieving favorable health outcomes. Timely detection through systematic screenings considerably reduces morbidity and mortality rates associated with oral malignancies. Patient education plays an essential role in raising awareness about the necessity of routine evaluations, emphasizing the potential for early intervention. Evidence indicates that informed patients are more likely to engage in preventive behaviors, thereby improving prognostic outcomes. In addition, community outreach initiatives can effectively augment access to screenings, particularly in underserved populations, addressing disparities in healthcare access. Clinical strategies must integrate thorough education and outreach programs to foster a culture of proactive health maintenance. Such efforts are instrumental in enhancing early detection and improving overall public health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Lifestyle Changes Can Reduce the Risk of Oral Cancer?
To mitigate oral cancer risk, evidence indicates that tobacco cessation and alcohol moderation are critical. Clinically, these lifestyle modifications greatly lower carcinogenic exposure, thereby reducing potential malignant transformations within oral epithelial tissues, according to current epidemiological and clinical studies.
Are There Natural Remedies to Help Prevent Oral Cancer?
Natural remedies for oral cancer prevention have been explored, focusing on antioxidant foods and herbal supplements. Clinical evidence suggests that incorporating these may help reduce risk, though they should complement, not replace, conventional medical advice and screenings.
How Often Should Someone With a Family History of Oral Cancer Get Screened?
Individuals with a family history of oral cancer should consider an annual screening frequency. This recommendation is based on evidence indicating increased risk within this population, necessitating regular evaluations to facilitate early detection and management of potential malignancies.
Can Diet Influence the Likelihood of Developing Oral Cancer?
Dietary patterns considerably influence oral cancer risk. Evidence-based research indicates that a diet high in fruits, vegetables, and antioxidants is associated with cancer prevention, while excessive alcohol and processed foods increase susceptibility from a clinical perspective.
Is There a Genetic Test Available for Oral Cancer Susceptibility?
Genetic testing for oral cancer susceptibility focuses on identifying genetic markers and hereditary factors. While research is ongoing, no definitive test currently exists. Potential markers are being explored for early detection and risk assessment in clinical settings.