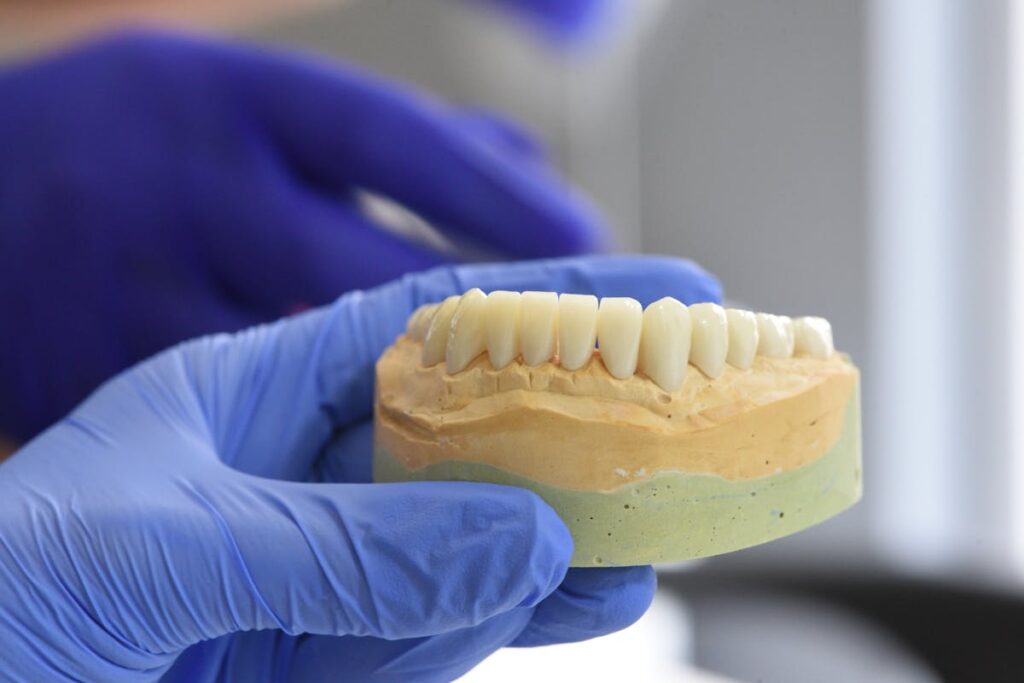
Dental implants and dentures are two common solutions for tooth replacement, each with distinct advantages. Dental implants, integrating with the jawbone, offer superior stability and a more natural appearance. In contrast, dentures may require frequent adjustments and can lead to discomfort or slippage. Implants promote oral health by preventing bone resorption, a significant factor for maintaining jaw integrity. Understanding these benefits is essential for informed decision-making in dental care.
Understanding Dental Implants
Dental implants, although a modern marvel in restorative dentistry, are grounded in decades of research and innovation. These fixtures are designed to mimic natural tooth roots and are typically fabricated from biocompatible titanium. The implant procedure involves surgical placement of the implant into the jawbone, followed by a process known as osseointegration, where the bone gradually fuses with the implant. This integration is critical for the implant’s stability and function.
The recovery timeline varies among patients, generally spanning several months. Initial healing occurs within weeks, but complete osseointegration can take up to six months. During this period, patients must adhere to specific post-operative care guidelines to optimize healing and reduce complications. Dental implants offer a durable, reliable solution for tooth replacement, considerably enhancing oral functionality and aesthetics.
Exploring Dentures
While dental implants are a remarkable advancement in tooth replacement technology, dentures remain a widely utilized alternative, offering a different approach to restoring oral function and aesthetics. Dentures, available in several types, including complete and partial options, cater to diverse patient needs. Complete dentures are suitable for individuals missing all teeth, whereas partial dentures are designed for those with some remaining natural teeth. Proper denture care is essential to guarantee their functionality and oral health. This includes regular cleaning to prevent bacterial accumulation, routine dental check-ups, and guaranteeing a proper fit to avoid discomfort. Evidence suggests that meticulous maintenance can enhance the comfort and effectiveness of dentures, supporting their viability as a reliable tooth replacement option for edentulous patients.
Durability and Longevity
When evaluating the durability and longevity of dental implants versus dentures, the material strength of implants, typically titanium, provides superior resistance to wear and tear compared to the acrylic or resin materials often used in dentures. Evidence suggests that with proper maintenance, dental implants can last several decades, whereas dentures may require more frequent adjustments or replacements. Patients are advised to contemplate the maintenance requirements of each option, as implants generally necessitate regular oral hygiene practices, while dentures require periodic relining and potential replacement.
Implant Material Strength
Although often considered a superior choice for tooth replacement, dental implants owe much of their reputation to the material strength that underpins their durability and longevity. The implant durability primarily derives from the utilization of titanium and zirconia, two material types known for their exceptional biocompatibility and mechanical properties. Titanium, widely used in medical applications, integrates seamlessly with bone, creating a stable foundation that can last several decades. Zirconia offers a metal-free alternative, providing comparable strength and an aesthetically pleasing appearance. Studies consistently demonstrate that these materials endure substantial functional loads, preserving their integrity over time. Patients benefit from reduced risk of fractures and long-term maintenance, enhancing quality of life by restoring dental function and confidence effectively.
Wear and Tear
Dental implants demonstrate remarkable resistance to wear and tear due to their composition and integration with the jawbone, which greatly contributes to their durability and longevity. Constructed from biocompatible materials like titanium, implants exhibit minimal wear patterns even under significant masticatory forces. The osseointegration process firmly anchors the implant, reducing micro-movements and subsequent material degradation. Unlike dentures, which are prone to abrasion and require periodic relining due to their susceptibility to wear patterns, implants maintain structural integrity over extended periods. Clinical studies highlight a low incidence of implant failure over decades, often due to external factors rather than intrinsic material degradation. Consequently, dental implants offer a robust, long-term solution for patients seeking reliable tooth replacement options with minimal deterioration over time.
Maintenance Requirements
Proper maintenance plays an essential role in preserving the durability and longevity of dental implants and dentures. Dental implants, composed of biocompatible materials like titanium, require minimal maintenance. Standard oral hygiene practices, such as brushing twice daily and regular flossing, suffice. The cleaning frequency mirrors that of natural teeth, reducing bacterial accumulation and preventing peri-implantitis. Conversely, dentures necessitate more rigorous care. Routine removal and thorough cleaning with appropriate solutions are vital to prevent microbial growth and staining. Their repair needs are comparatively higher due to potential wear, fractures, and fit adjustments over time. Evidence suggests that while implants offer long-term stability with minimal intervention, dentures demand consistent upkeep and periodic professional evaluations to guarantee peak functionality and comfort.
Aesthetics and Natural Appearance
The aesthetic considerations of tooth replacement options are critical to patient satisfaction and overall treatment success. Dental implants are renowned for restoring smile confidence due to their ability to mimic natural teeth closely. They integrate with the jawbone, preserving facial structure and preventing the bone resorption commonly associated with tooth loss. This integration supports the facial contours, maintaining a youthful appearance. In contrast, dentures may not offer the same level of aesthetic precision, often resulting in a less natural appearance. The acrylic base of dentures can sometimes detract from the overall esthetic outcome. Evidence suggests that patients with dental implants often report higher satisfaction levels concerning aesthetic outcomes compared to those with dentures, highlighting the implants’ superior ability to replicate natural dentition.
Comfort and Fit
When evaluating the comfort and fit of dental prosthetics, dental implants are often associated with a more natural feel and enhanced stability due to their osseointegration with the jawbone. This integration not only mimics the functionality of natural teeth but also offers significant long-term wear benefits, reducing the likelihood of slippage and discomfort commonly reported with dentures. Evidence suggests that patients with dental implants experience improved oral proprioception and a higher satisfaction rate regarding comfort compared to those using traditional dentures.
Natural Feel and Stability
Evaluating the natural feel and stability of dental implants versus dentures reveals considerable differences impacting patient comfort and fit. Dental implants, anchored directly into the jawbone, offer a natural sensation akin to that of original teeth. This osseointegration process guarantees a secure fit, minimizing movement and providing a stable foundation for biting and chewing. In contrast, traditional dentures rest on the gum line and may slip or shift during oral activities, potentially causing discomfort and reducing the natural sensation experienced by the patient. Evidence suggests that dental implants greatly improve masticatory function and speech clarity due to their stability. Patients often report enhanced confidence and satisfaction with dental implants, attributing this to their realistic feel and enduring fit compared to conventional dentures.
Long-term Wear Benefits
Patients seeking durable and comfortable dental solutions often consider the long-term wear benefits of dental implants and dentures. Dental implants, as a long-term investment, offer superior comfort through osseointegration, providing a stable and natural feel. This stability minimizes gum irritation and enhances chewing efficiency, which supports lifestyle adaptation without dietary restrictions. Evidence suggests implants require minimal adjustments over time, ensuring a consistent fit.
Conversely, dentures may necessitate periodic relining due to natural bone resorption, impacting their fit and comfort. Patients often need to adapt to lifestyle changes, such as avoiding certain foods to prevent dislodgement. Comparative studies highlight that while dentures generally incur lower initial costs, dental implants present a more favorable long-term solution for patients prioritizing comfort and functional efficiency.
Functionality and Oral Performance
While evaluating the differences in functionality and oral performance between dental implants and dentures, it is essential to think about their impact on masticatory efficiency and speech articulation. Dental implants offer significant functional advantages due to their osseointegration with the jawbone, resulting in enhanced stability and force transmission during mastication. This leads to superior masticatory efficiency compared to dentures, which may slip or require frequent adjustments. Performance comparison further highlights that dental implants more closely mimic natural teeth, providing patients with a seamless changeover, particularly in speech articulation. Dentures, though improved with recent advancements, still present challenges such as altered phonetics and reduced bite force. Hence, dental implants emerge as a preferable choice for those prioritizing functionality and oral performance.
Maintenance and Care
Although both dental implants and dentures require regular maintenance to guarantee oral health, their care routines differ significantly. Dental implants demand meticulous oral hygiene, similar to natural teeth. Brushing twice daily with a soft-bristle toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste, alongside regular flossing, is essential to prevent peri-implantitis—a condition akin to gum disease. Conversely, dentures necessitate removal and cleaning after meals. They should be brushed with a non-abrasive denture cleanser and soaked overnight in a denture solution to maintain their integrity and prevent bacterial buildup. Evidence suggests that inadequate cleaning routines for dentures can lead to stomatitis and other oral infections. Both options necessitate routine dental check-ups to monitor oral health, ensuring that any issues are addressed promptly for ideal patient outcomes.
Cost Considerations
Following the thorough maintenance and care required for dental implants and dentures, understanding the financial implications of each option is essential for patients. Dental implants often incur higher initial costs compared to dentures, reflecting the surgical procedures and materials involved. However, this expense can be offset over time by their longevity and reduced maintenance needs. Insurance coverage varies considerably; many plans offer partial coverage for dentures, while implant coverage is less common. Patients should investigate individual policy details to comprehend out-of-pocket expenses. Financing options, such as payment plans or dental loans, provide alternative methods to manage these costs. It is vital for patients to evaluate these financial aspects alongside clinical outcomes to make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs and resources.
Impact on Oral Health
Dental health professionals recognize the significant impact that dental implants and dentures can have on oral health. Dental implants offer superior benefits in maintaining gum health and promoting bone preservation. Implants integrate with the jawbone through osseointegration, providing stimulation that prevents bone resorption—a common issue with edentulism. This process is essential for preserving the structural integrity of the jawbone, subsequently supporting adjacent teeth and gum tissues. Conversely, dentures, while effective for tooth replacement, do not provide this stimulation, potentially leading to accelerated bone loss and compromised gum health. The absence of direct root replacement in dentures often results in reduced mechanical stability and may necessitate frequent adjustments. As a result, implants present a more sustainable solution for long-term oral health preservation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Dental Implants or Dentures Affect Speech Clarity?
Speech improvement and pronunciation issues are influenced by both dental implants and dentures. Dental implants, by restoring a stable oral environment, often enhance articulation, whereas dentures may initially present pronunciation challenges due to their less secure fit.
What Are the Dietary Restrictions With Implants and Dentures?
Both dental implants and dentures necessitate dietary adjustments. Implants allow for diverse food textures, enhancing chewing efficiency. Conversely, dentures may require soft foods initially, gradually introducing firmer textures to prevent appliance dislodgement and guarantee patient comfort.
How Does Smoking Impact Implants Vs Dentures?
Smoking effects greatly reduce implant success rates due to impaired healing and increased risk of peri-implantitis. Conversely, dentures are less affected by smoking, though it may still contribute to oral tissue irritation and hygiene complications.
Are There Age Limitations for Getting Dental Implants?
Age factors considerably influence implant eligibility, as bone density and health conditions vary with age. However, dental implants are generally feasible for adults with adequate bone support and overall health, regardless of age, following thorough clinical evaluations.
What Materials Are Used to Make Dental Implants and Dentures?
Dental implants primarily use titanium or zirconia for the implant materials due to their biocompatibility and strength. Denture types include complete or partial dentures, commonly made from acrylic resin, sometimes reinforced with metal for additional support.