Dental implants are a significant investment in oral health, yet their coverage by insurance remains a complex issue. Coverage varies widely depending on the type of insurance plan, such as PPOs, HMOs, or indemnity plans, and the specific terms outlined within each policy. Factors like medical necessity, pre-existing conditions, and annual limits can influence reimbursement. Patients must navigate these intricacies to determine potential financial responsibility, highlighting the importance of understanding one’s insurance policy thoroughly.
Understanding Dental Implants and Their Costs
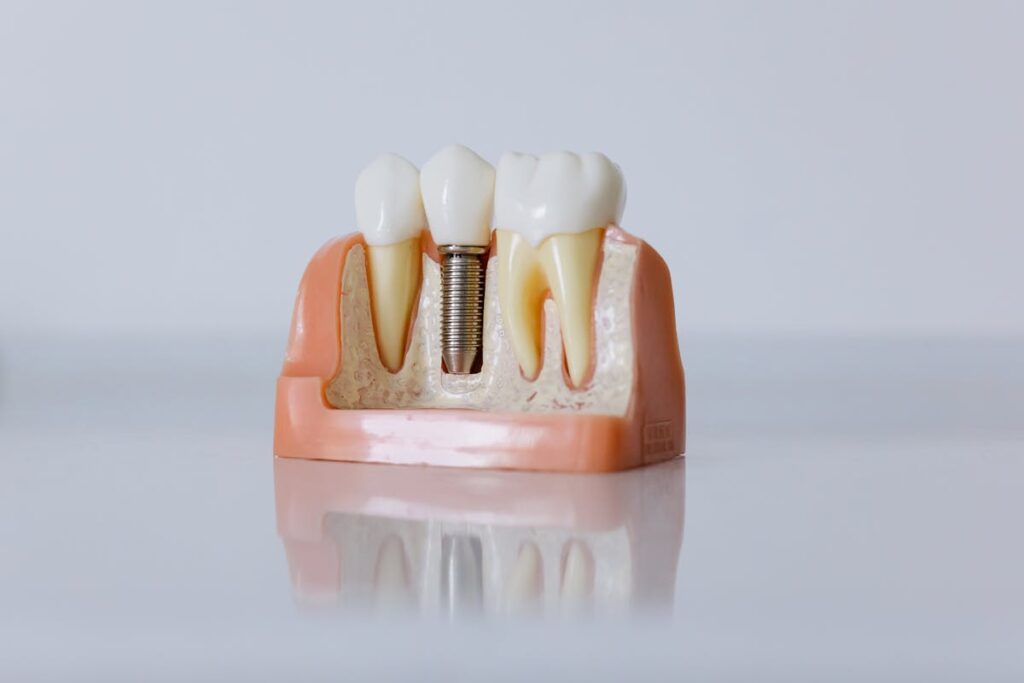
Although dental implants are a popular solution for tooth replacement, understanding their associated costs requires careful examination of various factors. Primarily, implant materials greatly influence the overall expense. Titanium, favored for its biocompatibility and durability, often incurs higher costs compared to alternative materials such as zirconia. The choice between these materials necessitates a thorough cost comparison to determine the best value for individual needs. In addition, the complexity of the procedure impacts the total expenditure. Advanced techniques or additional requirements like bone grafting elevate costs. Regional price variations also play a role, with urban centers typically presenting higher fees than rural areas. Consequently, a detailed analysis of these elements is essential for a precise estimation of dental implant expenses.
Types of Insurance Plans and Their Coverage
The landscape of dental insurance plans is varied, encompassing types such as Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs), Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs), and dental indemnity plans. Each plan type offers different levels of coverage for dental procedures, but coverage for dental implants specifically can vary considerably, often being limited or excluded. To make informed decisions, individuals must carefully assess the specific terms and conditions of their insurance plans regarding implant coverage.
Dental Insurance Plan Types
Steering through the complexities of dental insurance plans requires an understanding of the diverse types available and their respective coverage options. A thorough coverage comparison reveals three primary types: Dental Health Maintenance Organizations (DHMO), Preferred Provider Organizations (PPO), and indemnity plans. Each type presents distinct plan benefits. DHMOs typically offer lower premiums with restricted provider networks, emphasizing preventive care. PPOs provide greater flexibility in choosing providers, albeit with higher costs, allowing for a mix of in-network and out-of-network services. Indemnity plans, though less common, offer extensive provider choice but come with higher premiums and potential upfront costs. Evaluating each plan type’s benefits and constraints is essential for individuals seeking ideal coverage tailored to their dental health needs.
Coverage for Implants
Understanding the types of dental insurance plans provides a foundation for examining how they cover specific procedures, such as dental implants. Insurance plans, including Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs), Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs), and indemnity plans, vary in their coverage for dental implant types. PPOs often offer partial coverage, reimbursing a percentage of the procedure’s cost. HMOs typically require network providers, limiting reimbursement options for implants. Indemnity plans may offer more flexibility, albeit with higher out-of-pocket expenses. The insurance claim process for dental implants involves submitting detailed documentation, including treatment plans and cost estimates. Insurers evaluate these claims based on policy terms, pre-existing conditions, and annual limits. Understanding these parameters is essential for policyholders seeking reimbursement for dental implant procedures.
Factors That Affect Insurance Coverage for Implants
Although dental implants are a common solution for tooth replacement, their insurance coverage can be complex and varies considerably depending on several factors. Factors influencing coverage include the policyholder’s eligibility criteria and the specific terms outlined in their dental insurance policy. Insurance providers typically assess the medical necessity of the implant procedure, which may require thorough documentation from dental professionals. Some policies may distinguish between coverage for medical and purely cosmetic purposes, affecting eligibility for reimbursement. Additionally, pre-existing conditions and waiting periods can influence coverage decisions, as insurers often impose restrictions on pre-existing dental issues. The age of the patient and the overall health condition may also be considered when determining coverage eligibility. Understanding these factors is essential for managing dental implant insurance complexities.
Reviewing Your Specific Insurance Policy
When reviewing a specific insurance policy for dental implants, it is essential to analyze coverage limitations and exclusions that may impact the overall financial responsibility. Additionally, understanding pre-authorization requirements is vital, as these stipulations can affect the approval and timing of implant procedures. A thorough examination of these aspects guarantees a complete understanding of potential out-of-pocket expenses and procedural compliance.
Coverage Limitations and Exclusions
How thoroughly do dental insurance policies address the complexities of implant coverage? Analyzing coverage restrictions and policy nuances reveals significant variability across providers. Often, policies exclude certain implant-related procedures or impose strict limitations on reimbursement amounts. For instance, some plans may classify dental implants as cosmetic rather than essential, thereby restricting coverage altogether. Other policies might limit coverage to specific components of the implant process, such as excluding the crown or abutment. Additionally, lifetime maximums and waiting periods further complicate the landscape, affecting the financial feasibility for policyholders. Understanding these intricacies requires a methodical examination of the policy’s fine print, ensuring that individuals are informed of any exclusions or restrictions that could impact their anticipated benefits.
Pre-Authorization Requirements Needed
Why is pre-authorization a significant element in the dental insurance landscape? The pre-authorization process guarantees that dental procedures, such as implants, meet the criteria set by the insurance provider before treatment commences. This procedural step prevents unexpected expenses by confirming coverage eligibility upfront. Insurance verification plays a key role in this process, as it involves scrutinizing the policy details to ascertain what is covered under the plan. Typically, insurers require documentation from the dental provider, including diagnostic reports and treatment plans. This submission is then evaluated against policy guidelines. Failure to obtain pre-authorization may lead to denial of claims, resulting in significant out-of-pocket costs for patients. As a result, understanding pre-authorization requirements is essential for managing the complexities of dental insurance coverage effectively.
Common Exclusions and Limitations in Policies
Dental insurance policies frequently encompass a variety of exclusions and limitations, which can greatly impact coverage for implant procedures. Among the common exclusions are cosmetic surgeries, pre-existing conditions, and experimental treatments. These exclusions often result in policyholders bearing the full cost of dental implants. Moreover, policy limitations generally include annual maximums and waiting periods, which restrict the amount reimbursable within a specific timeframe. Such limitations can also encompass lifetime maximums specifically for implants, regardless of the overall dental coverage. Additionally, some policies may not cover related procedures like bone grafts or sinus lifts, which are integral to the implant process. Consequently, understanding these exclusions and limitations is essential for policyholders to manage expectations and financial planning effectively.
Exploring Partial Coverage Options
Often, dental insurance policies provide partial coverage options for implants, offering a strategic way to mitigate out-of-pocket expenses for policyholders. Coverage variations exist across different insurance providers, with some policies covering specific components of the implant procedure, such as the crown, abutment, or surgical placement. Typically, partial coverage may include a set percentage of the total cost, ranging from 20% to 50%, depending on the plan specifics. These options are contingent on factors such as annual maximums, deductibles, and waiting periods. Additionally, insurers may classify implants under major restorative procedures, impacting reimbursement rates. Understanding these partial coverage options requires careful examination of policy details to ascertain the extent of financial relief provided and to plan accordingly for any uncovered expenses.
Alternative Financing and Payment Plans
While partial insurance coverage can offset some costs associated with dental implants, many patients still face significant out-of-pocket expenses. To address this financial burden, various payment options and financing solutions are available. Dental practices often collaborate with third-party companies to offer patient-friendly financing plans. These plans may include low-interest monthly payments or deferred payment schedules, making them accessible to a broader demographic. Additionally, some dental offices provide in-house payment options, allowing patients to pay in manageable installments directly to the practice. Health care credit cards are another viable option, offering short-term, interest-free periods. Evaluating these diverse financing solutions enables patients to strategically manage expenses associated with dental implants, thereby facilitating access to necessary dental care without immediate financial strain.
Discussing Insurance and Coverage With Your Dentist
When considering dental implants, how does one effectively navigate the complexities of insurance coverage? A thorough discussion with a dentist is pivotal. Patients should prepare by understanding basic insurance terminology and compiling specific coverage questions. This includes inquiring about the dental office’s familiarity with various insurance providers and any pre-authorization requirements that might be necessary.
It is essential to determine whether the dental implants fall under cosmetic or restorative procedures, as this classification directly impacts coverage eligibility. Clarification on the extent of coverage for associated procedures, such as bone grafting, should also be obtained. Analyzing the policy’s annual maximum and any applicable deductibles is vital. Extensive communication guarantees that patients are well-informed of potential out-of-pocket expenses, facilitating informed financial planning.
Tips for Maximizing Your Insurance Benefits
Understanding the nuances of insurance coverage with a dentist lays the groundwork for optimizing insurance benefits. A critical step involves familiarizing oneself with insurance terminology to navigate policy details effectively. This includes understanding terms like “annual maximum,” “deductibles,” and “waiting periods.” Analyzing the claim process is imperative; it guarantees that all required documentation is correctly submitted and deadlines are met. Patients should inquire about pre-authorization requirements, as some procedures necessitate prior approval to qualify for coverage. Additionally, evaluating the insurer’s network of preferred providers can result in reduced out-of-pocket costs. Regular communication with the insurer and dental office aids in clarifying doubts, thereby minimizing errors in claims. Efficient coordination between these entities is essential to fully capitalize on potential benefits.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do Dental Implants Require a Referral From a Specialist?
The referral process for dental implants typically involves specialist requirements. General dentists often assess initial needs but may refer patients to oral surgeons or periodontists. This guarantees appropriate expertise and precision in implant placement and treatment planning.
How Long Is the Typical Waiting Period for Implant Coverage?
The typical waiting period for implant coverage varies widely, influenced by waiting period factors such as insurance provider policies and coverage variations. Some plans may impose a waiting period of 6 to 12 months before benefits activation.
Are There Any Age Restrictions for Insurance Coverage on Implants?
Current inquiries often explore age limitations impacting coverage eligibility for implants. Insurers may impose age-related criteria, potentially affecting both young and elderly candidates. Analyzing specific policy terms is essential to determine precise coverage eligibility concerning age factors.
Can I Appeal a Denied Insurance Claim for Dental Implants?
An appeal process exists for denied dental implant claims. It requires thorough claim documentation, including a detailed explanation of medical necessity, supporting evidence, and adherence to insurer guidelines, to effectively challenge the initial decision and seek reconsideration.
Does Implant Coverage Differ Between Individual and Family Plans?
The current question examines variations in dental implant coverage between individual coverage and family coverage. Differences may arise due to plan specifics, cost-sharing measures, and the overall policy structure. Thorough analysis of each plan’s details is necessary.